|
There are different types of stuttering. Neurogenic stuttering happens as a result of brain injury like stroke, and psychogenic stuttering is associated with psychiatric disease. But the most common type is developmental stuttering, which appears in children 2-4 years old as they are learning to speak. This type of stuttering is mainly genetic; some figures claim that it is up to 70% heritable. Scientists can determine heritability by performing twin studies, looking at the difference in frequency of the disorder between fraternal and identical twins.
Stuttering can become worse in stressful situations, but at its core, it is generally considered to be neural and not just due to anxiety. Developmental stuttering is associated with many brain structural abnormalities. In particular, the left inferior frontal gyrus of children who stutter has abnormal gray matter, and less white matter connecting it to the rest of the brain. This region is normally involved in language production, and is loosely related to the speech production region popularly known as “Broca’s area”. To learn more, visit the Stuttering Foundation.
0 Comments
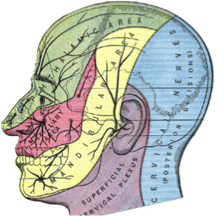
A headache is a perception of pain in the head, and can have a variety of causes, from stress and tension (the most common) to bacterial infections and tumors (rare), and even the over-use of some medications. Many are not well understood. However, many headaches involve something known as referred pain, or pain felt in a location different from its origin. For example, some headaches actually originate from neck or shoulder problems.
Tension-type headaches often come after stress and fatigue. People used to think they were caused by muscular tension, but new studies suggest that it might be the other way around; pain receptors activated in the head, neck, and shoulders can result in muscle tenderness. Over-sensitive pain receptors can start interpreting normal sensations as pain, and the headache can become chronic. We are still not sure what causes these pain receptors to be active in the first place. Migraines are recurring and very painful headaches that are often one-sided, last less than 72 hours, and can induce nausea and sensitivity to light or sound. Today, many scientists believe migraines are caused by a “wave” of activity in the brain (of unknown origin) that eventually activates pain receptors in the trigeminal nerve, a nerve responsible for transmitting touch and pain signals from the face. This spreading wave of abnormal brain activity is known as cortical spreading depression. |
Archives
June 2022
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed